| 1. Scope of the coverage: |
| This specification is pertinent to the application of metal
plate resistors ( designated as MPC ). |
| 2 .Temperature range of the application: |
| -55℃ ~ +155℃。 |
| 3. Type: |
| One type, normal size, of metal plate resistors
is offered in this specification (ref. to Table-1) |
| 4.Marking and illustration: |
| The designation method for MPC is by the alpheumeric marking
of black ink (Fig.1) |
 |
| |
| 5.Dimension, voltage, resistance range: listed in
the following Table Unit: mm |
| |
| Model |
Rated
Power
(W) |
Resistance
Range
(Ω) |
Tolerance |
Dimension (mm) |
| A |
B |
C |
d φ |
| MPC70 |
2 |
0.1~1.0 |
K |
8±1.0 |
13±1.0 |
4±0.5 |
0.6±0.1 |
| MPC76 |
2 |
0.01~0.05 |
K |
8±1.0 |
13±1.0 |
4±0.5 |
0.6±0.1 |
| MPC71 |
5 |
0.1~1.0 |
K |
18±1.0 |
14±1.0 |
5±0.5 |
0.6±0.1 |
| MPC75 |
5 |
0.01~0.08 |
K |
18±1.0 |
14±1.0 |
5±0.5 |
0.8±0.1 |
| MPC722
3-lead type |
10
|
0.1, 0.22, 0.33, 0.47 |
K
|
17±1.0
|
26±1.0
|
5±0.5
|
0.8±0.1 |
| MPC722
2-lead type
anti-stress lead |
10 |
0.47, 1.0, 1.2, 2.2, 3.3 |
J
|
18±1.0
|
26±1.0
|
5±0.5
|
1.0±0.1 |
|
| |
| 6.Characteristics of electrical performance |
| 6.1 Rated power |
| The rated power indicates the maximum power the resistor
can endure continuously when the |
| ambient temperature is equal to or lower than 70℃. When
the ambient temperature is higher than |
| 70℃, the rated power of the resistor is determined by the
derating curve described in the following |
| figure. |
 |
| |
| 6.2 Rated voltage |
| The rated voltage of a resistor is either a continuous
DC voltage or an AC rms voltage which can be |
| calculated by the following formula. If the calculated
rated voltage is higher than the highest |
| working voltage then the highest working voltage should
be used as the rated voltage. |
 P: Rated power (W) R: Nominal resistance
(Ω) E: Rated voltage (V) P: Rated power (W) R: Nominal resistance
(Ω) E: Rated voltage (V) |
| |
| 6.3 Insulation resistance (Ref. JIS C5202 5.6) |
| Equipment: Insulation resistance tester |
| The body of the resistor is wrapped around by the aluminum
foil without extending beyond the |
| resistor body. Clap one electrode on the aluminum foil
and the other electrode on the lead wire. |
| Apply 500V from the tester for 1 min. and the measured
resistance value should be larger than |
| ≧ 10MΩ. |
| |
| 6.4 Dielectric strength (Ref. JIS C5202 5.7) |
| Equipment: Dielectric strength tester |
| The body of the resistor is wrapped around by the aluminum
foil without extending beyond the |
| resistor body. Clap one electrode on the aluminum foil
and the other electrode on the lead wire. |
| Apply 500V from to the electrodes for 1 min. No flash-over,
burning or breakdown should be |
| observed. |
| |
| 6.5 Short time overload (SOL) (Ref. JIS C5202 5.5) |
| Equipment: S.O.L. tester. |
| Apply 2.5 times of rated voltage to the resistors for 5
seconds. If the applied voltage is larger than |
| the voltage listed in the following table, then the voltage
in the table should be used instead. After |
| the test, the sample should be stabilized at room temperature
for 30 min. before the resistance is |
| measured. The change of the resistance before and after
the test should be: ±(2%+0.1Ω). |
| |
| 7.Environmental tests |
| 7.1 Load life test (Endurance with rated load) (Ref. JIS
C5202 7.10) |
| Equipment: High temperature chamber and DC power supply |
| The resistors are put in a fixture where no interference
will be allowed. Put the fixture in a 70±3℃ |
chamber and apply rated voltage with a cycle of 90 min.
ON and 30 min. OFF for  hours.
hours. |
| After 240, 480, 720 and 1,000 hours, the resistors
are taken out and stabilize at room temperature |
| for 30 min. and then the resistance is measured. Upon each
step of resistance measurement, the |
| change of the resistance should not exceed ±(5%+0.1Ω) and
the appearance should show no |
| remarkable abnormality and legibility of marking. |
| |
| 7.2 Resistance to damp heat (Ref. To JIS C5202 7.2) |
| Equipment: Constant temperature and humidity chamber |
| The resistors are put in a 40±2℃ chamber with RH=90~95%
for 240±4 hours. After the test, take |
| the resistors out and stabilize in room temperature for
1 - 4 hour. Measure the resistance. The |
| acceptable change of resistance should not exceed ±(2%+0.1Ω)
and the appearance should show |
| no remarkable abnormality and legibility of marking. |
| |
| 7.3 Endurance under damp heat and load (Ref. JIS C5202
7.9) |
| Equipment: Constant temperature and humidity chamber, DC
power supply |
| The resistors are put in a fixture where no interference
will be allowed. Put the fixture in a 40±2℃ |
| chamber with RH=90~95% and apply rated voltage with a cycle
of 90 min. ON and 30 min. OFF for |
 hours. Water drops should avoid
dripping on the resistors. After 240 and 1,000 hours, the hours. Water drops should avoid
dripping on the resistors. After 240 and 1,000 hours, the
|
| resistors are taken out and stabilize at room
temperature for 1 hou-r and then the resistance is |
| measured. Upon each step of measurement, the change
of the resistance should not exceed |
| ±(5%+0.1Ω) and the appearance should show no
remarkable abnormality and legibility of marking. |
| |
| 7.4 Temperature coefficient (TCR) (Ref. JIS C5202 5.2) |
| Equipment: High temperature chamber |
| Measure the resistance at room temperature. Put
the resistor in a chamber with the temperature |
| of RT+100℃ for 30 - 45 min. to stabilize. Measure
the resistance again. Compare the resistance |
| at these two temperatures with the following equation
and the acceptable value is ±350 PPM/℃. |
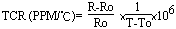 |
| R = Resistance at T T = RT + 100℃ Ro = Resistance
at To To =room temperature |
| |
| 7.5 Temperature cycling (Ref. JIS C5202 7.4) |
| Equipment: High temperature chamber, low temperature chamber |
| Measure the resistance before the test. Put the resistor
to -55℃ chamber for 30 min. then take it |
| out at room temperature for 2 to 3 min.. Put the resistor
to +155 ℃chamber for 30 min. then take it |
| out at room temperature for 2 to 3 min. This completes
a cycle. Repeat the cycle 5 times. Put |
| resistors at room temperature for 90 min. and then measure
the resistance. Compare the |
| resistance before and after test. The acceptable change
of resistance is ±(1%+0.05Ω). The |
| appearance should show no remarkable abnormality and legibility
of marking. |
| |
| 8. Mechanical performance |
| 8.1 Resistance to soldering heat (Ref. JIS C5202 6.4) |
| Equipment: Solder bath |
| Measure the resistance before the test. Immerse part of
the lead wire which is 4±0.8mm away from |
| the body to the flux for 5 - 10 sec. Take the resistor
out and immerse resistors in the solder bath of |
| 350±10℃ for 3.5±0.5 sec.. Stabilize at room temperature
for 1 hour and then measure the |
| resistance value. Compare the resistance values before
and after the test, The acceptable change |
| is ±(1%+0.05Ω). |
| |
| 8.2 Solderability (Ref. JIS C5202 6.5) |
| Equipment: Solder bath |
| Immerse part of the lead wire which is 4±0.8mm away from
the body to the flux for 5 - 10 sec. Take |
| the resistor out and immerse resistors in the solder bath
of 245±5℃ for 3.5±0.5 sec. Take the |
| resistor out and inspect the lead wire visually. The acceptable
level is the coverage of the new |
| solder to be 95%. The composition of the solder bath is
99.7% tin and 0.3% Cu. |
| |
| 8.3 Robustness of terminals (Ref. JIS C5202 6.1) |
| Tensile strength of termination |
| Equipment: Weight gauge |
| Fixed the resistor and apply axially along the lead wire
of 2.5Kg (0.8φ lead wire) or 1.0Kg (0.6φ lead |
| wire) for 30 sec. The lead wire should not break or detached
from the resistor and the change of |
| the resistance should be less than ±(0.5%+0.05Ω). |
| |



